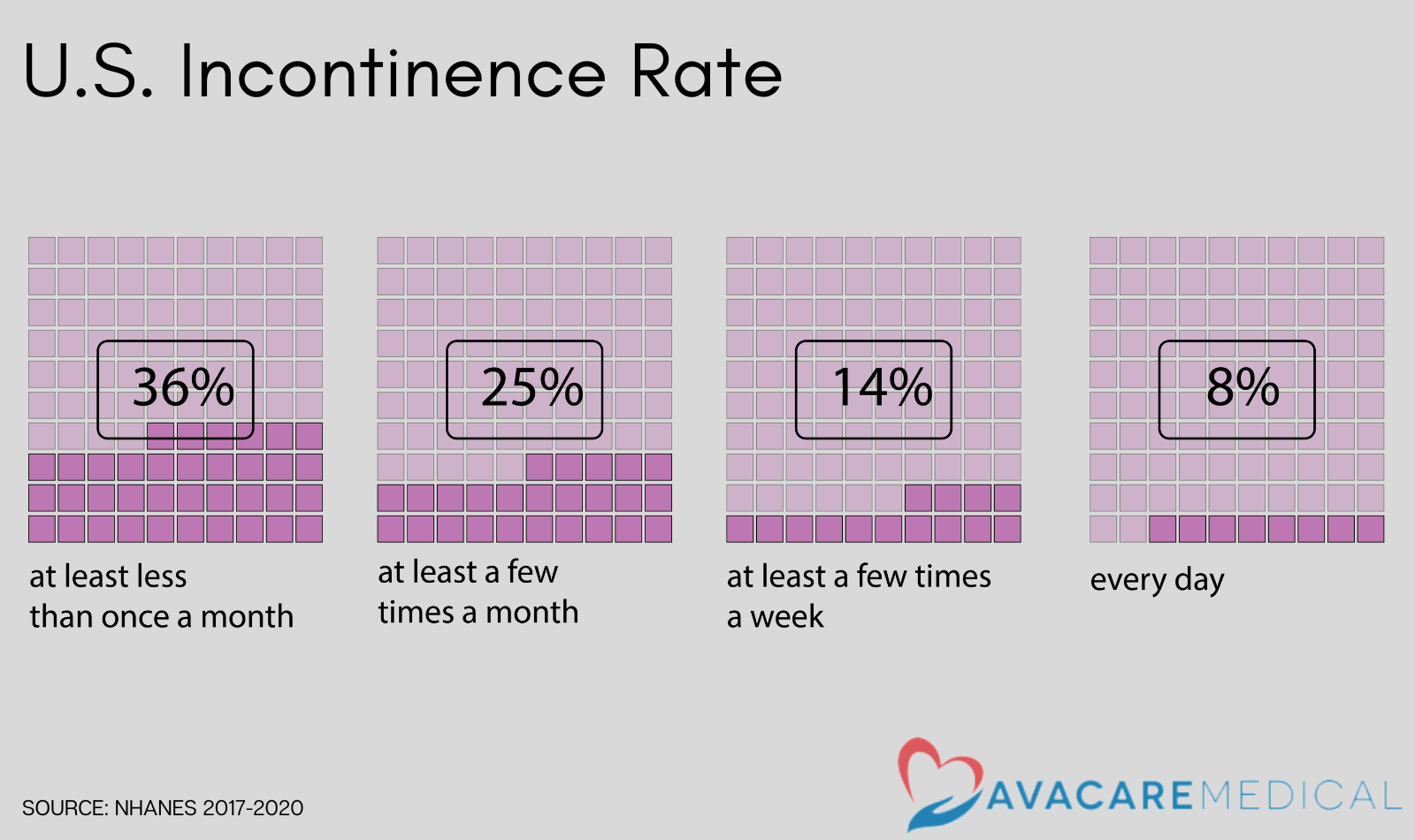
Incontinence, the loss of bladder function, is a condition that over 25 million Americans face. According to a recent NHANES survey, 36% of Americans reported involuntary urinary leakage at least less than once a month, 25% reported at least a few times a month, 14% reported at least a few times a week, and 8% reported involuntary urinary leakage every day.
In this study, we examined incontinence rates among adults in the US to assess the impact of gender, age, and weight on the individual’s likelihood of suffering from incontinence during their lifetime.
Key findings
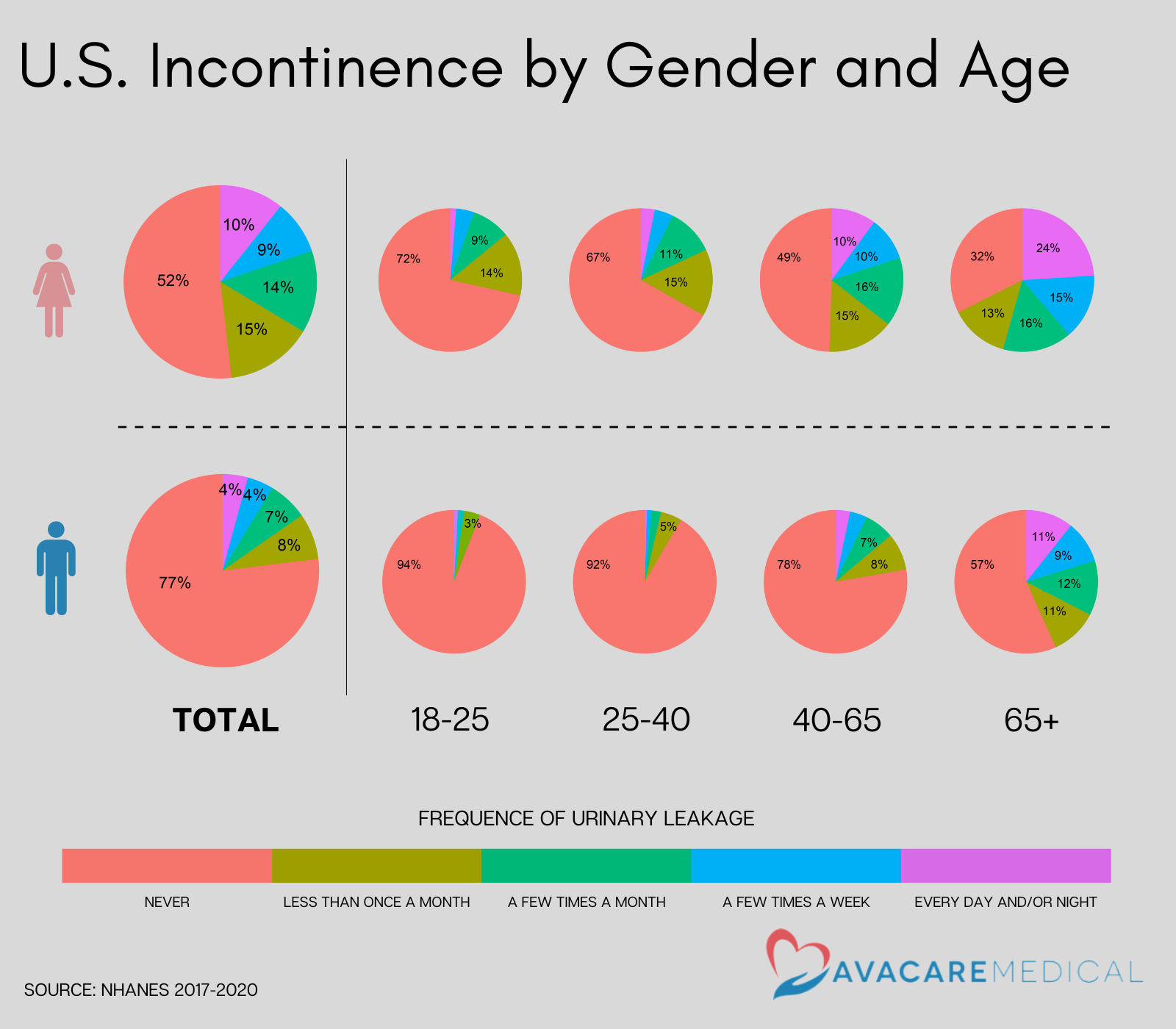
- American women are two times more likely to experience involuntary urine loss in their lifetime. 23% of American men and 48% of American women reported incontinence.
- As Americans age, the chance of facing incontinence increases. 30% of Americans below 65 years old reported involuntary urine loss, which increased to 55% for the population above 65 years old.
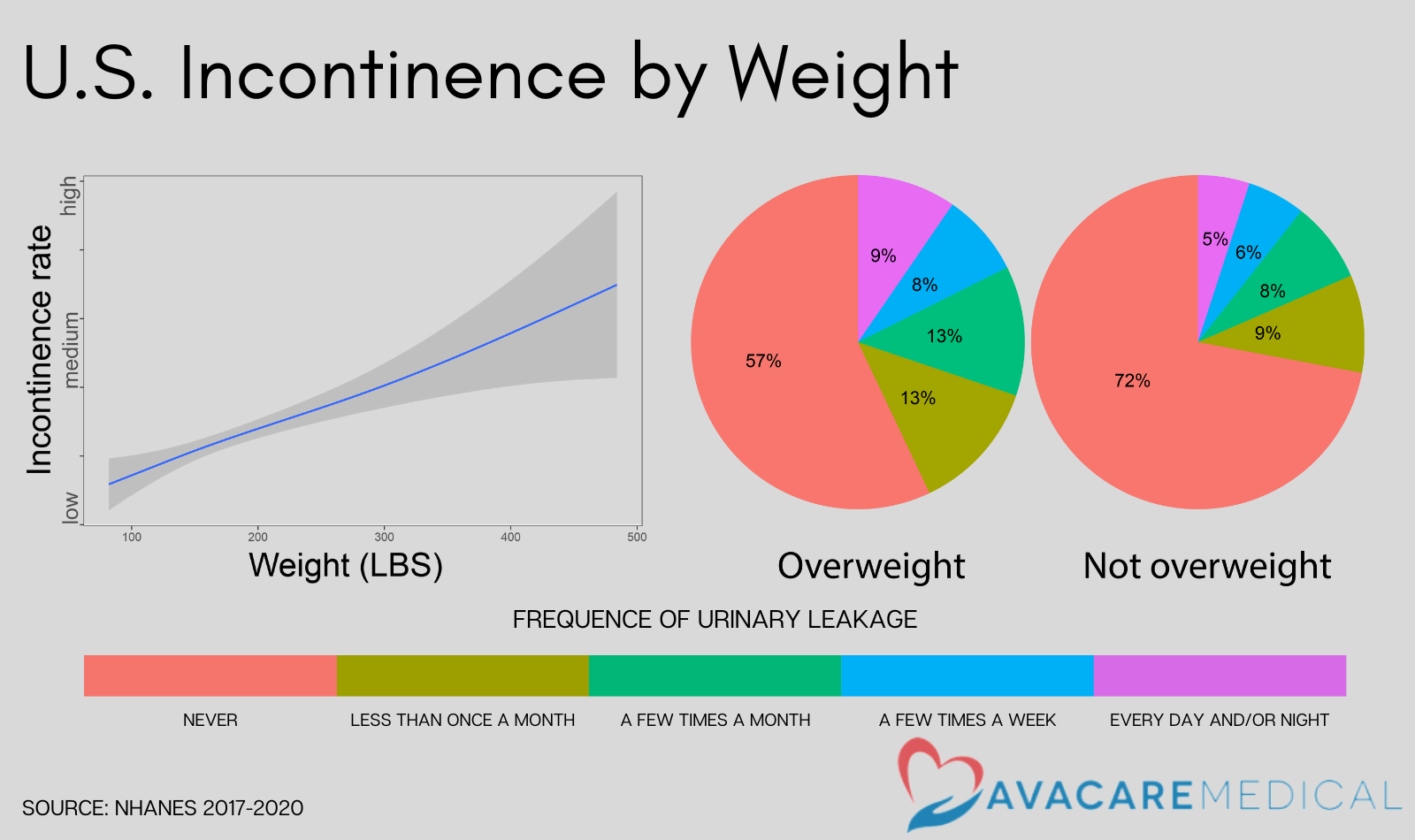
- Analysis showed that weight and incontinence increase together. While 28% of Americans who are not overweight reported incontinence, 43% of Americans in the overweight population reported incontinence.
Incontinence Types
Urinary incontinence is a common condition that affects people of all ages. There are several different types of urinary incontinence, each with its own set of symptoms and causes.
- Stress incontinence occurs when there is an unintentional leakage of urine when you exert pressure on your bladder, such as when you cough, sneeze, laugh, exercise, or lift something heavy. Stress incontinence is often caused by weakened pelvic muscles, which can be due to many reasons, such as pregnancy, childbirth, or other factors.
- Urge incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine after a sudden urge to urinate. This type of incontinence can be caused by a minor condition, such as a urinary tract infection, or a more severe condition, such as a neurological disorder or diabetes. People experiencing urge incontinence may need to urinate often, including throughout the night.
- Overflow incontinence is characterized by frequent or constant dribbling of urine due to a bladder that doesn’t empty completely. This type of incontinence can be caused by an obstruction in the urinary tract or a problem with the muscles that control the bladder.
- Functional incontinence refers to a type of urinary incontinence that is caused by a physical or mental impairment. This type of incontinence can occur when a person is not able to make it to the toilet in time due to a physical or mental impairment, such as arthritis, dementia, or spinal cord injury.
- Mixed incontinence is a combination of stress, urge, overflow, or functional incontinence.
Risk Factors
The main risk factors include biological sex, age, and being overweight.
According to a recent NHANES survey, women experience incontinence at a higher rate than men. 48% of American females and 23% of American males reported experiencing urinary leakage at least once a month. The difference between genders is most pronounced in early adulthood, with 6 out of 100 men experiencing involuntary urinary loss between the ages of 18 and 20, while women in the same age group experience incontinence about five times more. As Americans age, the ratio between biological sexes decreases, with older American women experiencing incontinence 1.5 times more than older men. The reported differences between genders arise from anatomical differences, pregnancy, and menopause.
Age plays a significant role in incontinence for both genders. As we age, the muscles in the bladder and urethra weaken, making older individuals more likely to experience involuntary leakage. Men over 40 are four times more likely to experience incontinence than those between the ages of 18 and 40. While only 8% of men under 40 reported incontinence at least once a month, 30% of men over 40 reported incontinence at least once a month. The pattern is less pronounced for women, with those over 40 being about twice as likely to have incontinence issues compared to women between 18 and 40. 56% of women over 40 reported incontinence at least once a month, compared to 31% of women under 40. The highest incontinence rates were observed by Americans aged 65 or above. 43% of the 65+ years men and 68% of the 65+ years women reported involuntary urinary leakage.
Being overweight puts pressure on the bladder, leading to a higher likelihood of incontinence. NHANES data shows that as weight increases, so does incontinence. According to the data, 43 out of 100 overweight Americans experience incontinence at least once a month, whereas only 28 out of 100 non-overweight Americans do. About 10% of overweight people experience incontinence daily, which is two times more than non-overweight Americans. Overall, being overweight increases the risk of incontinence by 1.5 times compared to those who are not overweight.
Conclusion
Millions of adult Americans across all age groups are experiencing continence-related issues on a monthly to daily basis. Research has shown that there are certain demographic factors and weight that can make individuals more likely to experience incontinence. Age is a strong predictor for both genders, with older individuals more likely to experience involuntary urinary leakage. Factors such as anatomical differences, pregnancy, and menopause may also play a role in the differences observed between genders. Overweight Americans are more likely to experience involuntary urinal leakage since there is more pressure on their bladder. It is important for individuals to be aware of these demographic factors and to seek appropriate treatment if they are experiencing incontinence.
Methodology
This analysis is based on data from the survey collected by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in the United States between 2017 and 2020.